AI’ Of The Storm – Market-Shaking Developments
1.1 Microsoft’s Majorana 1- Exploring The World’s First Quantum Computing Chip
Microsoft has announced a groundbreaking advancement in quantum computing with the development of Majorana 1, the world’s first quantum chip powered by a revolutionary Topological Core architecture. This innovation is poised to make industrial-scale quantum computing a reality within years rather than decades, addressing some of the most complex computational challenges faced today.
a) What is Majorana 1?
Majorana 1 represents a major milestone in quantum technology. It is the first quantum chip to leverage a topoconductor, a novel material capable of observing and controlling Majorana particles to produce more stable and scalable qubits. Qubits serve as the fundamental building blocks of quantum computers, and this breakthrough significantly enhances their reliability and scalability.
b) Understanding Topoconductors
A topoconductor, or topological superconductor, is a unique category of material that creates a completely new state of matter—distinct from solids, liquids, or gases—known as a topological state. This property allows for the development of more stable, faster, and digitally controlled qubits, eliminating many of the limitations associated with current quantum computing methods. A recent Nature paper details how Microsoft researchers successfully demonstrated the quantum properties of topological qubits and accurately measured them, marking a crucial step toward practical quantum computing.
c) How Was the Quantum Chip Developed?
The development of Majorana 1 required an entirely new materials stack, primarily composed of indium arsenide and aluminum. Microsoft fabricated these materials at an atomic level to engineer the Majorana particles necessary for advancing quantum computing.
The core of Microsoft’s topological qubit design consists of aluminum nanowires arranged in an “H” shape. Each “H” contains four controllable Majorana particles, forming a single qubit. These structures can be interconnected and tiled across the chip, allowing for an efficient and scalable quantum computing architecture.
According to Krysta Svore, Microsoft Technical Fellow, “We had to create a new state of matter to reach this point, but once achieved, the architecture itself is elegantly simple and scalable.”
d) The Quantum Ecosystem
The Majorana 1 chip functions within a sophisticated ecosystem, comprising:
- Control Logic to manage qubit operations
- A Dilution Refrigerator to maintain qubits at ultra-low temperatures, colder than outer space
- A Software Stack capable of integrating with AI and classical computing systems
Microsoft has meticulously developed or modified these components in-house to ensure seamless performance. However, refining this ecosystem and achieving large-scale implementation will still require further engineering efforts in the coming years.
e) Overcoming Challenges in Material Science
One of the biggest hurdles in creating topological qubits was perfecting the materials stack. Unlike traditional silicon-based computing, Microsoft’s topoconductor is built using indium arsenide, a material also used in infrared detectors. When cooled to extremely low temperatures, this semiconductor integrates with superconductors, forming a hybrid system that enables quantum coherence.
“We literally spray atoms one by one. If there are too many defects, the qubit becomes unusable,” explained Svore. “Ironically, this is why we need quantum computers—to predict and design even better materials for future quantum advancements.”
f) The Significance of the Topological Core
The Topological Core in Majorana 1 incorporates hardware-level error resistance, making the qubits inherently more stable. Commercially viable quantum applications require trillions of operations on a million qubits, which is impractical with existing methods that rely on fine-tuned analog control. By enabling digital qubit control, Microsoft’s approach simplifies and accelerates quantum computing progress.
Microsoft’s long-term bet on topological qubits—a high-risk, high-reward strategy—has started to pay off. The company has already integrated eight topological qubits onto a single chip and designed it for scalability up to one million qubits.
g) A Quantum Computer for Real-World Impact
Matthias Troyer, Microsoft Technical Fellow, emphasized that Microsoft’s goal has always been to create a quantum computer with real commercial impact rather than just an academic proof of concept. Recognizing the need for a fundamentally new type of qubit to achieve scalability, Microsoft worked closely with the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which funds breakthrough technologies for national security. This partnership is accelerating the development of commercially viable quantum computing solutions.
h) What Can This Quantum Chip Achieve?
Much like semiconductors revolutionized electronics, topoconductors could enable the quantum systems of the future. A quantum computer powered by a million qubits could tackle problems beyond the reach of all classical computers combined. Potential applications include:
- Breaking Down Microplastics into harmless byproducts
- Developing Self-Healing Materials for construction, healthcare, and manufacturing
- Optimizing Drug Discovery through advanced molecular simulations
According to Chetan Nayak, Microsoft Technical Fellow, “We asked ourselves, ‘What does the quantum transistor of the future need?’ This led us to a unique combination of materials and a scalable qubit architecture.”
i) The Future of Quantum Computing
The unveiling of Majorana 1 marks a major shift in the trajectory of quantum computing. By pioneering topological qubits and developing a scalable architecture, Microsoft has laid the foundation for quantum systems capable of addressing real-world challenges.
As Nayak put it, “Whatever you’re doing in quantum computing, it needs a clear path to a million qubits. Without it, you’ll hit a wall before solving the world’s most important problems. We’ve worked out that path.”
With Majorana 1, Microsoft has transformed the dream of large-scale, practical quantum computing into an imminent reality, paving the way for a future where quantum technology drives groundbreaking innovations across industries.
Table of Contents
1.2 The Deep Dive into Deepseek1.2 The Deep Dive into Deepseek
DeepSeek AI is like an uncharted ocean—its depths unknown, its mysteries endless. And yet, the curiosity to dive deeper, to uncover what lies beneath, is simply irresistible!
This Chinese open-source AI model is sending shivers down the spines of AI competitors and how! Deepseek has emerged as a formidable rival to ChatGPT, surprising the world with its efficiency while being developed at nearly half the cost of other leading AI models.
a) Deepseek explained in a nutshell
Let’s break it down with a simple analogy. Think of a Louis Vuitton bag—an iconic luxury brand that costs a fortune, symbolizes status, and is crafted with meticulous detail and investment. Now, imagine a nearly identical bag hitting the market. It looks just like Louis Vuitton, offers the same features and functionality, but here’s the catch—it costs a tenth of the price, requires minimal labor to produce, and skyrockets in demand due to its affordability.
That, in essence, is what’s happening in the AI world. OpenAI, the original powerhouse, stands as the luxury brand, while DeepSeek, the new player, emerges as the strikingly similar yet significantly cheaper alternative, shaking up the competition.
Deepseek, a powerful open-source model from China is making waves as it has been built in a record time of just two months, with an investment under $6 million. Yup, read that again. This is more than just an AI breakthrough- it is a drastic shift in the market that challenges the belief that only by investing billions can corporations come up with groundbreaking AI softwares. Deepseek’s speciality is that it is open-sourced, meaning that anyone can access it, modify it and customize it. This kind of transparency is definitely a game-changer and openly challenges big techs like Google and Microsoft that have invested billions to come up with softwares.
As for its functionality, Deepseek can do reasoning- breaking down problems into logical steps; text-based tasks- writing emails, essays, and creative writing; Request handling- analyze incoming requests, detect the topic, urgency, and key details, and then assign them to the right person/ department; personalized recommendations- provide customized suggestions based on user interactions and more.
b) Under the Radar: Scrutiny Over Data Practices
As the saying goes, the grass is always greener on the other side. While Deepseek initially celebrated its success in the AI industry, it is now facing mounting scrutiny over data privacy concerns. Several countries have raised alarms about the security risks posed by the Chinese-developed AI model, leading to bans and restrictions, particularly on government devices. The primary concern revolves around the lack of transparency in how Deepseek collects, stores, and utilizes user data. According to its privacy policy, Deepseek gathers personal information such as email addresses, phone numbers, passwords, and dates of birth for registration purposes. Additionally, it collects chat history, including both text and audio inputs, along with technical data such as IP addresses, keystroke patterns, and details about users’ operating systems.
In response to these concerns, governments across multiple nations have taken precautionary measures, with some implementing outright bans.
- United States
 In the United States, lawmakers are deliberating on a bill that would prohibit Deepseek on all government-owned systems. The urgency of these concerns became evident when NASA – National Aeronautics and Space Administration officially blocked Deepseek from its networks and employee devices on January 31. Just a week prior, the U.S. Navy had issued an internal warning against using the AI model, citing potential security and ethical risks tied to its origin and functionality. These actions indicate a growing hesitation within U.S. agencies regarding AI applications with opaque data policies.
In the United States, lawmakers are deliberating on a bill that would prohibit Deepseek on all government-owned systems. The urgency of these concerns became evident when NASA – National Aeronautics and Space Administration officially blocked Deepseek from its networks and employee devices on January 31. Just a week prior, the U.S. Navy had issued an internal warning against using the AI model, citing potential security and ethical risks tied to its origin and functionality. These actions indicate a growing hesitation within U.S. agencies regarding AI applications with opaque data policies.
- South Korea
South Korea has also taken a strong stance against Deepseek, with the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy temporarily restricting its use on employee devices due to security concerns. The government has advised ministries and agencies to exercise caution when using AI programs, including Deepseek and ChatGPT. On January 31, the country’s Personal Information Protection Commission formally reached out to Deepseek, requesting clarification on how it manages user data. Meanwhile, Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power, a state-run entity, has already blocked Deepseek across its internal systems, signaling a broader move within the country to limit potential cybersecurity risks.
- Australia
Australia has also joined the list of countries banning Deepseek from government use. The Department of Home Affairs issued a directive requiring all government agencies to prevent the use, installation, and access to Deepseek applications and services. Additionally, all existing instances of Deepseek have been ordered to be removed from government systems and devices. Australian Home Affairs Minister Tony Burke justified the decision by stating that the ban was essential to protect the nation’s security and interests, reinforcing the country’s proactive approach toward cybersecurity threats.
- Italy
Italy has followed suit by imposing strict limitations on Deepseek’s ability to process user data within its jurisdiction. On January 30, the Italian Data Protection Authority, known as Garante, restricted Deepseek’s operations in the country due to a lack of transparency regarding how personal data is managed. This action came just two days after the regulator sought detailed responses from the Chinese startup about its data storage and processing practices. Italy’s decision underscores the broader European concerns regarding AI governance and data privacy, particularly when dealing with foreign technology companies.
- Taiwan
Taiwan has also moved swiftly to curb Deepseek’s influence by blocking its use across all government departments. Authorities cited security vulnerabilities as the primary reason for this action, reinforcing the country’s cautious stance on foreign AI applications that do not provide clear data-handling policies. The Taiwanese government’s decision aligns with similar moves by other nations that are prioritizing national security over the rapid adoption of emerging AI technologies.
c) So where is Deepseek headed?
With multiple countries already moving to ban Deepseek, the real question now is whether the software can maintain its relevance in the ever-evolving AI landscape. Despite facing restrictions from major global players, this Chinese startup has developed a groundbreaking model that may not suffer significant losses in the long run. The reason? Deepseek’s open-source nature sets it apart from many proprietary AI models, making it widely accessible to researchers, developers, and organizations worldwide.
By choosing an open-source approach, Deepseek has sparked an important debate—could this be the future of AI? Will major tech giants eventually shift toward open-source AI development, recognizing its potential to foster global collaboration and accelerate technological advancements? The open-source model allows for widespread innovation, enabling developers from different parts of the world to experiment, modify, and improve upon existing frameworks. This could lead to faster breakthroughs in AI, possibly pushing industry leaders like Google, Microsoft, and OpenAI to rethink their current proprietary models.
However, there is another dimension to this development. With Deepseek’s architecture freely available, major corporations or even government-backed entities might simply customize the model to create their own AI systems—perhaps even more powerful and sophisticated ones. This, in turn, could pose a competitive threat to Deepseek itself. While the company may have pioneered this AI model, it is entirely possible that enhanced versions built upon its framework could overshadow it, raising questions about its long-term dominance.
That being said, the global bans on Deepseek do not necessarily signal the end of its influence. Instead, they highlight the complex dynamics of AI governance, data security, and international competition. Despite regulatory hurdles, Deepseek’s model will likely continue to be leveraged in some capacity, either by organizations in countries that have not imposed bans or by private entities repurposing its framework for their own advancements.
In the grand scheme of things, AI development is a race that no country wants to fall behind in. While Deepseek’s future remains uncertain in certain regions, its impact on the AI industry is undeniable. Whether it thrives as an open-source pioneer or gets overtaken by more refined versions, one thing is certain—its role in shaping the AI landscape is far from over.
Only time will tell how this unfolds.
What do you guys think? Is Deepseek here to say? Tell us in the comments below!
d) Let’s address another very important question: Is DeepSeek Truly Transparent?
One of Deepseek’s strongest selling points has been its claim of robust data security. But is this truly the case? The reality of its data handling practices has been exposed by IT trainer and YouTuber David Bombal, who conducted an independent investigation to test these claims. Using an Ethernet cable to connect his Android phone to the internet, he employed a wiretap to monitor network traffic and analyzed the data flow with Wireshark, a powerful network analysis tool.
What he uncovered was deeply concerning. Wireshark Foundation detected 51 data packets being transmitted directly to Beijing—despite Deepseek’s assurance that no user data is sent to China. Further analysis revealed that Alibaba Cloud was also being used as an intermediary for data transmission, raising serious concerns about how the company handles sensitive user information.
In his video, Bombal made it explicitly clear that Deepseek’s claims of privacy and data protection are in direct contradiction with the evidence he gathered. If an independent researcher could uncover such alarming data transfers, it raises an important question—how much more could be happening behind the scenes?
e) Our two cents
This revelation underscores the growing challenge of data security in AI development. Users place immense trust in these platforms, often without a full understanding of how their data is stored, processed, and transmitted. In an era where data privacy is paramount, companies that fail to uphold transparency risk not only regulatory scrutiny but also a massive loss of credibility.
If Deepseek hopes to maintain its standing in the AI space, it must address these concerns head-on. Otherwise, its so-called “strongest USP” may turn out to be its biggest liability.
e) Perplexity Outsmarts DeepSeek
A well-deserved shoutout to Perplexity and its co-founder, Aravind Srinivas, for not only taking on Deepseek but doing so with remarkable audacity. In a landscape where competition is fierce, Perplexity has outmaneuvered Deepseek at its own game, proving that bold moves can redefine the industry. After all, they say everything is fair in love and war—and AI innovation, it seems, is no exception.
While Deepseek continues to be mired in controversy over its safety and data privacy concerns, Perplexity wasted no time in capitalizing on the moment. The AI research company swiftly introduced a modified version of Deepseek R1 within its own platform, offering users a more secure and transparent alternative. As promised by Srinivas, this version eliminates censorship restrictions, allowing open discussions on sensitive topics, including the Tiananmen Square incident—something Deepseek does not permit.
Beyond lifting content restrictions, Perplexity also tackled one of the biggest concerns surrounding Deepseek: data privacy. Unlike its competitor, which has been accused of transmitting user data to China, Perplexity assures that all user data remains securely stored in the United States. This decisive move not only challenges Deepseek’s dominance but also raises an important question—will other AI companies follow suit and adopt similar transparency-driven models?
“All DeepSeek usage in Perplexity is through models hosted in data centers in the USA and Europe. DeepSeek is open-source. None of your data goes to China,” wrote Srinivas on LinkedIn.
Perplexity’s co-founder took to X (formerly Twitter) to personally reassure users that the model integrated into their platform remains completely uncensored. To back up this claim, he shared a screenshot of an uncensored response, providing clear evidence that the version of Deepseek R1 used by Perplexity operates without censorship.
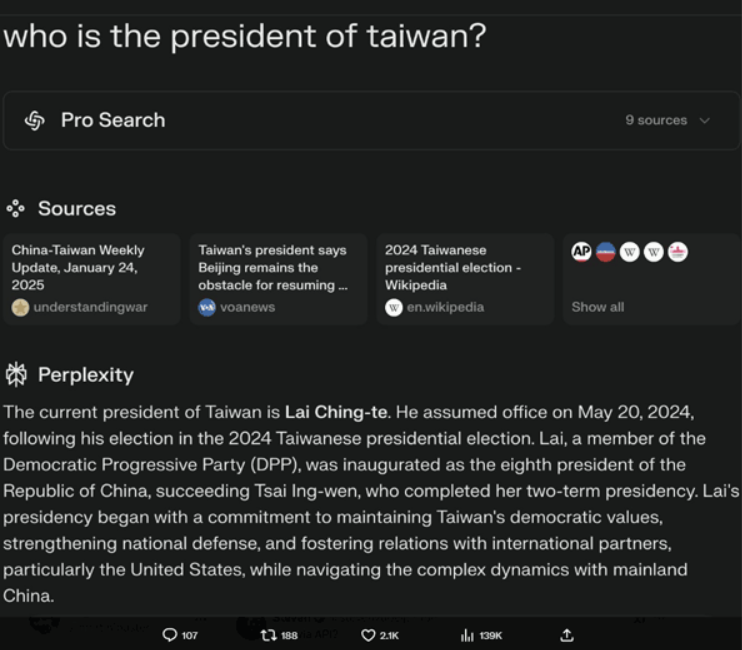 With this bold step, Perplexity has set a new precedent in AI ethics and security. Whether this will spark a larger shift in the industry remains to be seen, but one thing is certain—Deepseek has met its match.
With this bold step, Perplexity has set a new precedent in AI ethics and security. Whether this will spark a larger shift in the industry remains to be seen, but one thing is certain—Deepseek has met its match.
1.3 OpenAI Strikes Back
a) Deep vs. Deep: OpenAI’s Response’
Deepseek has positioned itself as a direct competitor to OpenAI, leveraging its rival’s model at a fraction of the cost and labor. Its arrival sent shockwaves through the AI industry, leading many to speculate that OpenAI might struggle to maintain its dominance. However, instead of showing signs of concern, OpenAI responded with confidence, unveiling a new research tool—aptly named Deep Research—designed to counter Deepseek’s rise.
This AI agent is engineered to gather and synthesize vast amounts of information from across the internet, producing research-grade reports comparable to those created by professional analysts. It’s a clear demonstration that OpenAI is not backing down from the challenge but rather stepping up its game.
When Deepseek first launched, speculation was rife that OpenAI’s influence would wane. Yet, in a bold and self-assured response, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman dismissed these concerns, stating that the company would soon “deliver much better models” and “pull up some releases.” This statement not only reinforced OpenAI’s resilience but also signaled its aggressive intent to stay ahead in the AI race.
However, we can’t ignore the fact that while Operator entered the market with a lot of “rizz,” its buzz fizzled out pretty soon, owing to its nascent stages and it being slightly challenging to operate. We went through some reviews of the software and here is what consumers are saying:
One can clearly see that Operator is still in the research preview stage, as OpenAI has stated. At this point, its practical use for real tasks seems limited.
The user went on to report 3 problems:
- Browser Navigation
While it may seem straightforward to us, the web is actually quite messy. Interfaces vary, clickable elements differ from site to site, and navigation isn’t always intuitive. Operators struggle significantly with this, often failing tasks simply because they can’t properly interact with certain forms or navigation structures.
- The VM Isn’t Your Computer
I had hoped to connect Operator to my Google Workspace Gmail account to automatically fetch receipts. However, signing in proved nearly impossible due to the challenges of interacting with the virtual machine.
- Reasoning
Operator is supposedly powered by GPT-4o, but based on its performance, that’s hard to believe—it feels like a major step backward. Web-based tasks go beyond simple searches; finding alternatives to a product, for example, requires understanding which sites offer better insights and why checking multiple sources matters. Operator lacks this awareness, leading to low-quality results.
- The Good News
Fortunately, these challenges are solvable, and improvements could come quickly. Browser interaction is difficult but not an insurmountable problem, and better reasoning is already present in other models.
“These improvements will happen, and I can already see many use cases for a working Operator. I very much look forward to it,” wrote a user.
In another review, a user reported that
“In all, I found that using Operator was usually more trouble than it was worth. Most of what it did for me I could have done faster myself, with fewer headaches. Even when it worked, it asked for so many confirmations and reassurances before acting that I felt less like I had a virtual assistant and more like I was supervising the world’s most insecure intern.”
This is, of course, early days for A.I. agents. A.I. products tend to improve from version to version, and it’s a good bet that the next iterations of Operator will be better. But in its current form, Operator is more an intriguing demo than a product I’d recommend using — and definitely not something most people need to spend $200 a month on.”
From the looks of it, it seems like at the first go, Open AI Operator is nothing big to arrive home at but definitely shows some immense potential.
While such advancements undeniably make life more convenient, they also raise an important question—are we becoming overly reliant on AI to handle even the most basic tasks?
More importantly, this rapid-fire response from OpenAI underscores a broader trend: the AI industry’s growing focus on competition over ethical considerations. It brings us back to the critical question—are we merely witnessing a race to the top, with ethical concerns sidelined in the process? While these innovations undoubtedly benefit humanity, they also come with significant risks. Deepseek has already sparked major privacy concerns worldwide. If AI development continues to prioritize dominance over responsibility, who will truly benefit in the long run? And at what cost?
b) Taking the AI game to the next level: Upcoming AI tools by OpenAI
As of February 2025, OpenAI has announced several upcoming tools and initiatives slated for release later this year:
- Custom AI Chip Development: OpenAI is advancing towards launching its in-house AI chip, aiming to start production next year. The design is expected to be finalized soon and subsequently sent for fabrication to the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co TSMC using advanced 3-nanometer technology. Initially, the chips will be used on a limited scale primarily to run AI models and could feature high-bandwidth memory and extensive networking capabilities. The development team, led by former Google TPU engineer Richard Ho, has doubled in size to 40 people. OpenAI’s move to develop its own chip reflects a broader trend among tech giants investing heavily in AI infrastructure amid debates on the necessity of expansive chip purchases.
- Stargate-like AI Program in Europe: OpenAI’s CEO Sam Altman expressed interest in bringing a Stargate-like artificial intelligence (AI) program to Europe, stating that his company would welcome the initiative. Stargate is a U.S. program initiated by President Donald Trump, supported by entities such as OpenAI, SoftBank Group Corp., and Oracle, with an investment plan of up to $500 billion in AI infrastructure over five years. Speaking at the Technical University of Berlin, Altman emphasized the need for European collaboration to establish AI regulations suited to the continent’s needs. Additionally, OpenAI announced the opening of a new office in Munich, furthering their European expansion which began with offices in Dublin and London in 2023, and in Paris and Brussels in 2024.
1.4 Mini Tools, Macro Outcomes: The o3-Mini Model
Another banger by Open AI is the recently launched o3-mini, which is its latest reasoning model. Here’s the reasoning model, explained by OpenAI’s chatbot:
“OpenAI o3-mini, is the newest, most cost-efficient model in our reasoning series, available in both ChatGPT and the API today. Previewed in December 2024, this powerful and fast model advances the boundaries of what small models can achieve, delivering exceptional STEM capabilities—with particular strength in science, math, and coding—all while maintaining the low cost and reduced latency of OpenAI o1-mini.
OpenAI o3-mini is our first small reasoning model that supports highly requested developer features including function calling, Structured Outputs, and developer messages, making it production-ready out of the gate. Like OpenAI o1-mini and OpenAI o1-preview, o3-mini will support streaming. Also, developers can choose between three reasoning effort, options—low, medium, and high—to optimize for their specific use cases. This flexibility allows o3-mini to “think harder” when tackling complex challenges or prioritize speed when latency is a concern. o3-mini does not support vision capabilities, so developers should continue using OpenAI o1 for visual reasoning tasks. o3-mini is rolling out in the Chat Completions API, Assistants API, and Batch API to select developers in API usage tiers 3-5
OpenAI’s o3-mini model, launched on January 31, 2025, is now available to ChatGPT Plus, Team, and Pro users, with Enterprise access. This model replaces the previous o1-mini in the model picker, offering higher rate limits and lower latency, making it particularly effective for coding, STEM, and logical problem-solving tasks. As part of this upgrade, daily message limits for Plus and Team users have been tripled from 50 to 150 messages. Additionally, o3-mini integrates search capabilities, allowing it to provide up-to-date answers with links to relevant web sources. This feature is currently in an early prototype stage as OpenAI works to enhance search integration across its reasoning models.
Free plan users can also try OpenAI o3-mini by selecting ‘Reason’ in the message composer or by regenerating a response. This marks the first time a reasoning model has been made available to free users in ChatGPT.
While OpenAI o1 remains our broader general knowledge reasoning model, OpenAI o3-mini provides a specialized alternative for technical domains requiring precision and speed. In ChatGPT, o3-mini uses medium reasoning effort to provide a balanced trade-off between speed and accuracy. All paid users will also have the option of selecting o3-mini-high in the model picker for a higher-intelligence version that takes a little longer to generate responses. Pro users will have unlimited access to both o3-mini and o3-mini-high.”
1.5 When AI Gets Political
Just when it seemed like OpenAI had reached the peak of its innovations, the company has once again outdone itself. It has now introduced ChatGPT Gov, a specialized, secure version of its widely popular chatbot, designed specifically for U.S. government agencies. This move marks a significant step in integrating artificial intelligence into public sector operations while maintaining the highest standards of security and compliance.
ChatGPT Gov is tailored to meet the stringent security needs of government entities while granting them access to OpenAI’s most advanced large language models (LLMs). According to OpenAI, this customized version enables agencies to operate within their own secure hosting environments, ensuring that sensitive, non-public data remains protected.
a) Does the U.S. Government Need ChatGPT Gov?
OpenAI strongly believes that the adoption of artificial intelligence by the U.S. government will enhance efficiency, streamline workflows, and boost productivity. In an official statement, the company asserted:
“We believe the U.S. government’s adoption of artificial intelligence can boost efficiency and productivity and is crucial for maintaining and enhancing America’s global leadership in this technology. This includes making our models available to support public sector work that benefits society – such as public health, energy and the environment, transportation and infrastructure, consumer protection, and national security.”
By leveraging ChatGPT Gov, government agencies can automate administrative processes, analyze vast amounts of data, improve decision-making, and provide better public services. The ability to harness AI for tasks such as policy drafting, cybersecurity threat detection, and multilingual translation could significantly enhance governmental operations.
b) Key Features of ChatGPT Gov
ChatGPT Gov is equipped with an array of features designed to support government agencies efficiently. Some of its standout capabilities include:
- Secure Collaboration: Teams can securely save and share conversations within a controlled workspace, fostering collaboration without compromising security.
- File Uploads: Users can upload text and image files for AI-powered analysis, allowing for quick data interpretation and decision-making.
- Access to GPT-4o: The latest and most powerful iteration of OpenAI’s language model, GPT-4o, provides advanced capabilities in text interpretation, summarization, coding, image analysis, and mathematical computations.
- Custom AI Models: Agencies have the ability to build, modify, and share their own custom AI models tailored to their specific operational needs.
- Advanced Administrative Controls: IT teams can manage users, configure security settings, and enable Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication, ensuring smooth and secure access management.
c) How Secure Is ChatGPT Gov?
Security is paramount when AI is deployed for government use, especially when dealing with highly sensitive information. OpenAI reassures agencies that ChatGPT Gov has been designed with state-of-the-art security measures to mitigate any risk of data breaches.
To ensure top-tier security, ChatGPT Gov operates on Microsoft Azure’s Government Cloud and Commercial Cloud through the Azure OpenAI Service. These platforms comply with the most stringent security protocols widely adopted by federal agencies.
Moreover, government agencies have the flexibility to implement their own security frameworks, including:
- IL5 (Impact Level 5): A security classification required for defense-related data.
- CJIS (Criminal Justice Information Services): Security compliance for law enforcement agencies.
- ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations): Regulations governing the control of defense-related data.
- FedRAMP High (Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program): A high-level security standard for cloud computing services.
While OpenAI supplies the AI models, government agencies retain full control over security, privacy, and compliance requirements, ensuring that their operational data remains fully protected.
d) Which Government Agencies Are Already Using AI?
Several government agencies have already begun integrating AI into their operations, leveraging its capabilities for a variety of applications. Some notable examples include:
- U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory: Utilizing ChatGPT Enterprise for administrative tasks, resource accessibility, and basic coding assignments.
- Los Alamos National Laboratory: Implementing AI to drive scientific research and innovation.
- Minnesota’s Enterprise Translations Office: Using ChatGPT Team for multilingual translation services to improve communication.
Commonwealth of Pennsylvania: Leveraging ChatGPT Enterprise to analyze project requirements and enhance workflow efficiency.
1.6 Meta’s Race to Catch Up
The global AI race is no longer just a matter of technological advancement; it has become a battleground between the United States and China, that comprise the world’s two largest economies. Over the past decade, China has raced ahead in AI research, funding, and implementation, backed by strong government policies and massive datasets from its vast population. Chinese companies such as Baidu, Tencent, and Alibaba, along with research powerhouses such as Tsinghua University, have rapidly advanced in areas like generative AI, computer vision, and natural language processing.
One of the most notable areas where China has outsmarted the US is in AI-powered surveillance. The Chinese government has leveraged AI to enhance public security through facial recognition technology and predictive policing. Additionally, Chinese AI companies have been able to scale innovation at an extraordinary rate due to strong support from the state and lower regulatory constraints.
In response to realise this gap, the US has taken aggressive steps to catch up. President Trump’s administration has increased federal funding for AI research and development, while major US tech giants like OpenAI, Google Google DeepMind, and Meta have ramped up their investments in AI-driven projects. The launch of the $500 billion Stargate AI infrastructure project, backed by OpenAI, SoftBank, and Oracle, exemplifies the US’s commitment to remain on top of the AI race.
However, what’s interesting is that American companies are now looking to China for inspiration. From scaling AI models efficiently to optimizing computational costs, firms in Silicon Valley are keen to adapt China’s strategies to stay relevant.
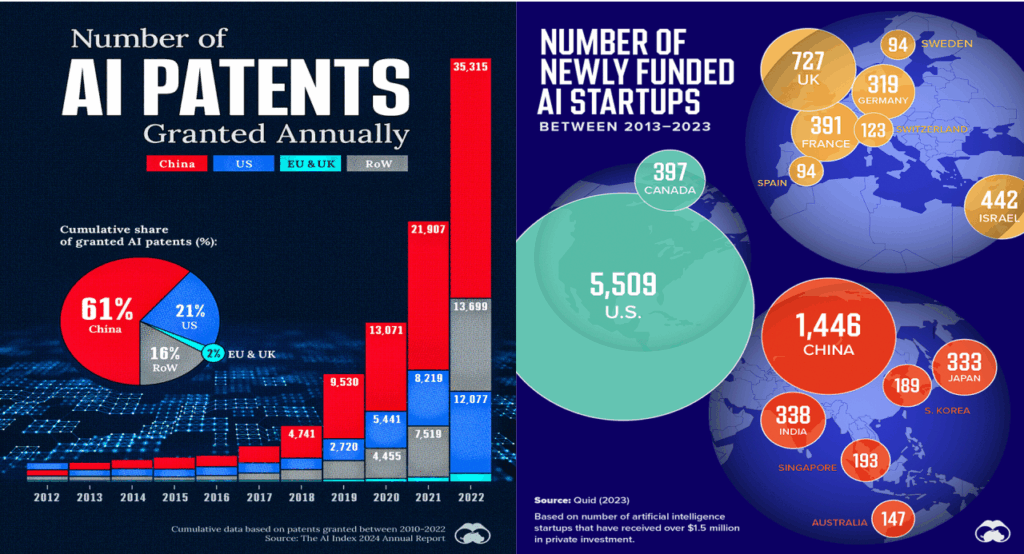
In the global race for artificial intelligence (AI) supremacy, patent filings serve as a key indicator of innovation and technological advancement. Recent data reveals that China has taken a commanding lead over the United States in AI-related patent applications, particularly in the realm of generative AI.
a) China’s Dominance in AI Patent Filings
Between 2014 and 2023, China filed over 38,000 patents for generative AI technologies, accounting for approximately 70% of the world’s total in this category. In contrast, the United States filed 6,276 patents during the same period, placing it a distant second.
This trend is consistent across the broader AI sector. In 2024 alone, China filed 300,510 AI-related patents, significantly outpacing the 67,773 patents filed by the United States.
b) Quality vs. Quantity
While China’s volume of AI patent filings is impressive, it’s essential to consider the impact and quality of these patents. American AI patents are cited nearly seven times more often than their Chinese counterparts, with an average of 13.18 citations per U.S. patent compared to 1.90 for Chinese patents.
c) Implications for the AI Landscape
China’s rapid accumulation of AI patents reflects its strategic emphasis on becoming a global leader in AI technology. However, the higher citation rate of U.S. patents suggests that American innovations may have a more significant influence on the field. This dynamic highlights the different approaches each country takes toward AI development: China focuses on broad, rapid advancements, while the U.S. emphasizes impactful, high-quality innovations.
As the AI landscape continues to evolve, both nations are likely to learn from each other’s strategies, potentially leading to a more balanced and collaborative global AI ecosystem.
The rapid rise of Deepseek has shook the best of the best players in the AI game. This also includes Mark Zuckerberg, the founder of Facebook, who has been putting together ‘war rooms’ of engineers, in a bid to figure how Deepseek was able to turn the world of AI upside down overnight, challenging big techs, that too at a fraction of the price.
According to Fortune, Zuckerberg assembled four war rooms, where one of the two teams was trying to decipher how the cost of training and running DeepSeek was lowered by high-flyer. The goal of this deliberation was to figure out a way to use the same tactics for Llama, as cited by an anonymous Meta employee.
Among the two remaining teams, one was trying to figure out which data did Deepseek use to train its model while the other was diving deep into how Llama can restructure its models based on attributes of the DeepSeek models, as reported by The Information.
Reportedly, Meta AI infrastructure director Mathew Oldham informed his colleagues that DeepSeek’s newest model could outperform even the next version of Meta’s Llama AI, which Zuckerberg hinted could be released in early 2025.
In a statement to The Information, a Meta spokesperson said, “We regularly evaluate all competitive models in our development process and have done so since [the company’s] Gen Al [group] was formed. Llama has been foundational in establishing the ecosystem for open-source AI models and we couldn’t be more excited to extend this leadership with the upcoming release of Llama 4.”
Zuckerberg announced that the company would be spending as much as $65 billion on projects related to AI in the coming year, including construction of a large data center and more AI hires. This announcement came days after OpenAI, in partnership with SoftBank, Oracle, and others, announced a $500 billion White House–backed AI infrastructure project called Stargate that will build dozens of new data centers across the U.S.
1.7 Deepseek’s Disruptive Entry into the AI Market: A Game-Changer for China’s Tech Sector
Ever since Deepseek emerged in the AI landscape, China’s major corporations have accelerated their AI adoption, signaling a transformative shift in the region’s tech ecosystem. Prominent industry leaders, including Great Wall Motor and the country’s top telecom providers, have integrated Deepseek’s AI model into their operations, showcasing the growing dominance of homegrown AI solutions in China’s AI revolution.
a) Major Companies Embrace Deepseek’s AI Model
China’s first publicly listed automaker, Great Wall Motor, has confirmed the integration of Deepseek AI into its connected vehicle system, branded as “Coffee Intelligence.” This marks a significant leap in AI-powered automotive technology, enhancing autonomous driving, in-car personalization, and predictive analytics.
The government is also playing a pivotal role in fostering AI adoption. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has emphasized the need for widespread AI implementation, with China’s three largest telecom companies—China Mobile, China Unicom, and China Telecom—actively incorporating Deepseek’s open-source AI model into their networks. This initiative aligns with Beijing’s broader strategy of reducing dependence on Western AI technologies and strengthening domestic innovation.
b) Market Impact: A Surge in AI Investments
Deepseek’s rapid ascent has triggered a wave of investor enthusiasm, leading to speculation about its potential long-term benefits for China’s broader tech sector. As a result, Chinese investors, chipmakers, software developers, and data center operators are aggressively pursuing AI-related stocks, seeing Deepseek as a catalyst for growth in the country’s digital economy.
Two publicly listed companies, however, have issued cautionary statements to temper investor expectations:
- Capital Online Data Service, a Beijing-based cloud computing provider, confirmed the deployment of Deepseek-R1 but admitted that the financial impact remains uncertain. Despite this, the company’s stock surged 49% in just two days.
- Shenzhen-based MeiG Smart Technology, which specializes in IoT connectivity, disclosed that it was working on Deepseek model adaptations, though still in the early development stages with no immediate business impact. This, however, did not stop its shares from jumping 33% within two days.
The speculative frenzy underscores investor optimism, but also raises questions about the sustainability of AI-driven market hype.
c) Tech Giants Join the AI Race
Deepseek’s momentum extends beyond the automotive and telecom industries. Chinese tech powerhouses Tencent and Huawei have also integrated Deepseek’s AI model into their offerings, demonstrating the growing influence of the startup across multiple industries. As Beijing continues to back indigenous AI initiatives, it is evident that Deepseek is not just a fleeting disruptor but a central force shaping China’s AI-powered future.
d) China’s AI Moment Has Arrived
Deepseek’s rapid adoption by major corporations and its soaring market impact highlight a crucial shift in China’s AI strategy: a decisive move toward self-reliance in artificial intelligence. By fostering homegrown AI development and integration, China is not just catching up with Western AI powerhouses—it is actively positioning itself as a global leader in AI innovation.
However, the exuberance surrounding Deepseek also carries risks. The surge in AI-related stock prices, despite companies cautioning against immediate financial gains, suggests a market fueled by speculation rather than tangible business outcomes. While Deepseek has undeniably ignited an AI revolution, the challenge now lies in translating hype into sustainable, long-term technological advancement.
In the end, China’s AI evolution will not be determined by short-term market gains, but by the real-world impact of AI-driven solutions. If Deepseek can maintain its technological edge and deliver meaningful innovation, it has the potential to reshape global AI economics—and possibly challenge Western dominance in artificial intelligence.
1.8 Why 75% of Businesses Are Failing to See AI ROI—And What the Winning 25% Are Doing Differently
A recent study revealed a striking reality: 75% of businesses are not achieving the expected returns on their AI investments. This highlights a crucial gap between AI adoption and effective implementation, emphasizing the need for better strategies, clearer priorities, and more realistic expectations when integrating AI into business operations.
a) The AI Hype vs. the Harsh Reality
Over the past two years, generative AI has been met with overwhelming admiration and enthusiasm within the U.S. tech community. Industry leaders have closely monitored each other’s advancements, often rushing to replicate successful breakthroughs. Investors and analysts have largely celebrated AI’s potential, fueling optimism about its transformative power.
However, this optimism faltered when Chinese AI startup Deepseek made its debut. While U.S. tech leaders acknowledged its innovation, their response was lukewarm at best. More importantly, Deepseek’s emergence triggered hesitation among American investors, causing a noticeable pullback that weighed down the stock market. This reaction underscores a growing uncertainty about the global AI race and its potential implications for Western dominance.
b) AI Investments Are Growing, But ROI Remains Elusive
A Boston Consulting Group (BCG) study examined global AI adoption trends and found that one in three companies plans to invest at least $25 million in AI upgrades this year. Despite these aggressive investments, only 25% of businesses are seeing meaningful returns, primarily big tech giants like Microsoft and Meta.
So, what separates this elite 25% from the struggling majority? The answer lies in their strategic approach to AI deployment.
c) What the 25% Are Doing Right
They Focus on Business Value, Not Just Technology
Leading AI adopters don’t get caught up in the hype of AI models and features. Instead, they start with fundamental business questions:
- Where are the major inefficiencies in our operations?
- How can we improve customer value?
- If we address specific pain points, how does that give us a competitive edge?
This approach ensures that AI is a tool for solving real business challenges, rather than just a shiny new technology experiment.
d) They Go Deep, Not Wide
Rather than experimenting with dozens of AI use cases, successful companies pick a few and go all in. They approach AI as a workflow transformation, committing time, resources, and personnel to ensure long-term success.
In contrast, companies that struggle with AI tend to spread themselves too thin—running short pilots across multiple use cases without prioritization or long-term commitment. As a result, their AI initiatives fail to generate lasting impact.
e) They Target Core Processes
The most successful AI-driven companies are ruthlessly focused on high-value workflows. They identify where AI can create the most impact and double down on those areas.
For example:
- Insurance companies prioritize underwriting and claims processing.
- Software firms enhance engineering efficiency.
- Retailers optimize supply chain and personalization engines.
Instead of treating AI as a side project, they embed it into the very foundation of their business operations.
f) They Rethink Workflows and Align Incentives
Winning companies don’t just layer AI onto existing workflows—they redesign them from the ground up. They also adjust incentives to ensure employees embrace AI-driven changes rather than resist them. This level of commitment and agility allows them to fully leverage AI’s potential.
g) AI Success Requires Strategy, Not Just Investment
The stark divide between AI winners and losers is not about how much money is spent, but how wisely it’s invested. Companies throwing money at AI without a clear strategy will continue to see disappointing returns. On the other hand, businesses that take a disciplined, value-driven approach—focusing on core processes, long-term commitment, and end-to-end workflow transformation—will reap significant rewards.
The bottom line? AI isn’t a magic bullet—it’s a tool. And like any tool, its success depends on how well it’s used.
1.9 Market Impact of AI Developments
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping global markets, influencing sectors beyond traditional technology industries. This comprehensive analysis delves into key statistics, market movements, and strategic recommendations for businesses navigating the evolving AI landscape.
Key Statistics
a) Return on Investment (ROI) in AI
- Global Perspective: A study by Boston Consulting Group found that only 25% of companies are currently achieving positive ROI from their AI investments, indicating that a majority are struggling to realize anticipated benefits.
- Asia-Pacific Region: Research from IBM reveals that just 11% of enterprises across the Asia-Pacific region expect to see the benefits of their AI adoption within the next two years, underscoring challenges in effective implementation.
b) Venture Capital (VC) Funding in AI
- Europe: In 2024, AI startups in Europe attracted $8 billion in venture capital, accounting for approximately 20% of all VC funding in the region, reflecting strong investor confidence.
- Global Trends: Globally, VC funding for AI startups rose to $131.5 billion in 2024, marking a 52% increase from the previous year, despite a 10% decline in overall startup funding, highlighting AI’s prominence.
c) Market Valuations and Stock Movements
- NVIDIA’s Recovery: NVIDIA has rebounded significantly from its previous $630 billion loss, driven by increased AI infrastructure investments from U.S. tech giants. As of March 3, 2025, NVIDIA’s market capitalization stands at approximately $2.783 trillion, making it the world’s third most valuable company. This resurgence underscores NVIDIA’s pivotal role in the burgeoning AI industry.
- In related developments, AI startup Anthropic recently raised $3.5 billion in a Series E funding round, achieving a valuation of $61.5 billion. This substantial investment highlights the escalating interest and confidence in AI technologies.
- Anthropic’s Projections: AI startup Anthropic forecasts its revenue could reach up to $34.5 billion by 2027, with a base scenario of increasing revenue to $12 billion in 2027 from $2.2 billion in 2025, underscoring anticipated rapid growth.
d) Corporate AI Investment Plans for 2025
- Amazon: Plans to invest over $100 billion in AI and cloud expansion, focusing on Amazon Web Services (AWS) , highlighting the company’s commitment to integrating AI into its services.
- Microsoft: Committed $80 billion for AI-related investments, with more than half targeted at U.S.-based projects, focusing on expanding AI workloads in its cloud infrastructure.
- Alphabet (Google): Set to spend $75 billion in capital expenditures, primarily to enhance technical infrastructure, including servers, data centers, and networking, to support AI initiatives.
- Meta (Facebook): Allocated between $60 billion and $65 billion for AI expansion, indicating a significant focus on integrating AI into its platforms.
e) Projected Global AI Investment
Goldman Sachs Analysis: Investment in AI is ramping up quickly and could eventually have an even bigger impact on GDP. Generative AI has enormous economic potential and could boost global labor productivity by more than 1 percentage point a year in the decade following widespread usage. For large-scale transformation to happen, businesses will need to make significant upfront investment in physical, digital, and human capital to acquire and implement new technologies and reshape business processes.
Those investments, which could amount to around $200 billion globally by 2025, will probably happen before adoption and efficiency gains start driving major gains in productivity. AI-related investment is climbing from a relatively low starting point and will likely take a few years to have a major impact on the economy. The U.S. is positioned as the market leader in AI technology, and American companies will likely be relatively early adopters. While a similar effect could also play out in other AI leaders (such as China), the investment impact will likely be smaller and more delayed. Over the longer-term, AI-related investment could peak as high as 2.5 to 4% of GDP in the U.S. and 1.5 to 2.5% of GDP in other major AI leaders, if AI growth projections are fully realized.
While the timing of the AI investment cycle is hard to predict, business surveys suggest that it’s likely to start having an investment impact in the second half of this decade, with earlier adoption by larger firms in information and professional, scientific, and technical services. Even though it will take time for AI to boost productivity, market interest in AI has already increased rapidly, with more than 16% of companies in the Russell 3000 index mentioning the technology on earnings calls, up from less than just 1% of those firms in 2016.
Roughly half of that spike came after the release of ChatGPT in the fourth quarter of 2022. Such mentions tend to predict increases in company-level capital spending. Incorporating that information, along with revenue growth projections for key AI-exposed businesses, AI investment could approach $100 billion in the U.S. and $200 billion globally by 2025. Despite this extremely fast growth, the near-term GDP impact is likely to be fairly modest given that AI-related investment currently accounts for a very low share of U.S. and global GDP.
AI investment is expected to be concentrated in four key business segments: companies that train and develop AI models, those that supply the infrastructure (for example, data centers) to run AI applications, companies that develop software to run AI-enabled applications, and enterprise end-users that pay for those software and cloud infrastructure services. AI investment thus far has been focused on model development, but a substantially larger hardware and software push will likely be required for generative AI to scale.
There are signs of early AI adoption in a few industries, even as the broader macro effects are still a few years off. Previous breakthroughs in technology show it’s hard to predict when adoption will increase enough to meaningfully nudge the economy. The productivity effects of the electric motor and personal computer only showed up in the macro data once about half of U.S. businesses had adopted the technology. In the 2021 American Business survey, only 4% of US firms reported using AI in their business processes. Likewise, CEO surveys show less than a quarter expect generative AI will impact their company or lower their labor needs over the next one to three years.
f) Strategic Recommendations
Given the challenges in achieving ROI, businesses should prioritize meticulous planning and strategic implementation of AI solutions. Rather than hastily adopting AI for the sake of innovation, companies should conduct comprehensive feasibility studies to assess AI readiness. Defining clear objectives aligned with business goals ensures that AI integration adds tangible value. Implementing pilot projects before scaling AI solutions enterprise-wide can help mitigate risks, while developing robust monitoring mechanisms allows organizations to track performance and fine-tune AI models over time.
As AI adoption expands, the demand for skilled AI professionals is outpacing supply. Businesses must address the talent gap by offering AI and data science training programs to existing employees. Partnering with educational institutions can foster AI talent development, and encouraging cross-functional AI literacy ensures smooth collaboration between AI specialists and domain experts. Creating AI centers of excellence within organizations can drive best practices and innovation, helping businesses stay ahead in the AI revolution.
AI-driven businesses heavily rely on data quality, security, and governance. To maximize AI’s potential, organizations should establish scalable and secure data storage solutions. Implementing strict data governance policies ensures compliance with privacy regulations, while enhancing data integration across departments can improve decision-making. Leveraging synthetic data can also help address data scarcity and bias in AI models, ensuring more accurate and ethical AI applications.
With increasing scrutiny on AI ethics and bias, organizations need to proactively implement responsible AI practices. Developing AI models with fairness, transparency, and accountability at the core is essential. Compliance with AI-related regulations, such as the EU AI Act and emerging global policies, should be a priority. Conducting regular audits can help detect and mitigate AI biases, and establishing AI ethics committees ensures responsible AI use and decision-making.
AI is redefining traditional business models, and companies must stay agile to remain competitive. Identifying AI-driven revenue streams, such as AI-powered SaaS solutions, automation-based cost savings, and AI-driven personalization services, can open new growth opportunities. Leveraging AI to improve customer engagement through chatbots, predictive analytics, and hyper-personalized experiences enhances user satisfaction. Forming partnerships with AI startups allows companies to access cutting-edge innovations, while continuously analyzing competitors’ AI strategies ensures they stay ahead in the evolving landscape.
To support AI expansion, organizations must scale their IT infrastructure by investing in high-performance computing resources for AI model training and deployment. Utilizing cloud-based AI services can reduce costs and improve flexibility, while optimizing AI workflows with edge computing allows real-time data processing. Collaborating with cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud enables businesses to maximize AI capabilities and improve operational efficiency.
AI has the potential to drive sustainability initiatives across industries. Implementing AI-driven energy optimization in data centers and industrial processes can reduce environmental impact. Using AI for predictive maintenance enhances efficiency and minimizes waste. AI can also optimize supply chain management for sustainable sourcing and logistics, while its role in climate modeling supports environmental conservation efforts.
The rapid evolution of AI presents both opportunities and challenges for businesses worldwide. While AI investment is surging, achieving sustainable growth requires a well-defined strategy, robust infrastructure, and a commitment to responsible AI practices. Companies that successfully integrate AI with a strategic approach will position themselves as leaders in the next wave of technological transformation. By focusing on implementation, workforce upskilling, ethical considerations, and business model adaptation, organizations can unlock AI’s full potential and drive long-term success in an increasingly AI-driven world.
1.10 OpenAI CEO Sam Altman Confirms GPT-5 Will Be Powered by O3 Reasoning Model—And It’s Free!
The AI world has been buzzing ever since Chinese startup Deepseek disrupted the industry with its groundbreaking advancements. Now, all eyes are on OpenAI and its CEO Sam Altman to respond—and it seems they have!
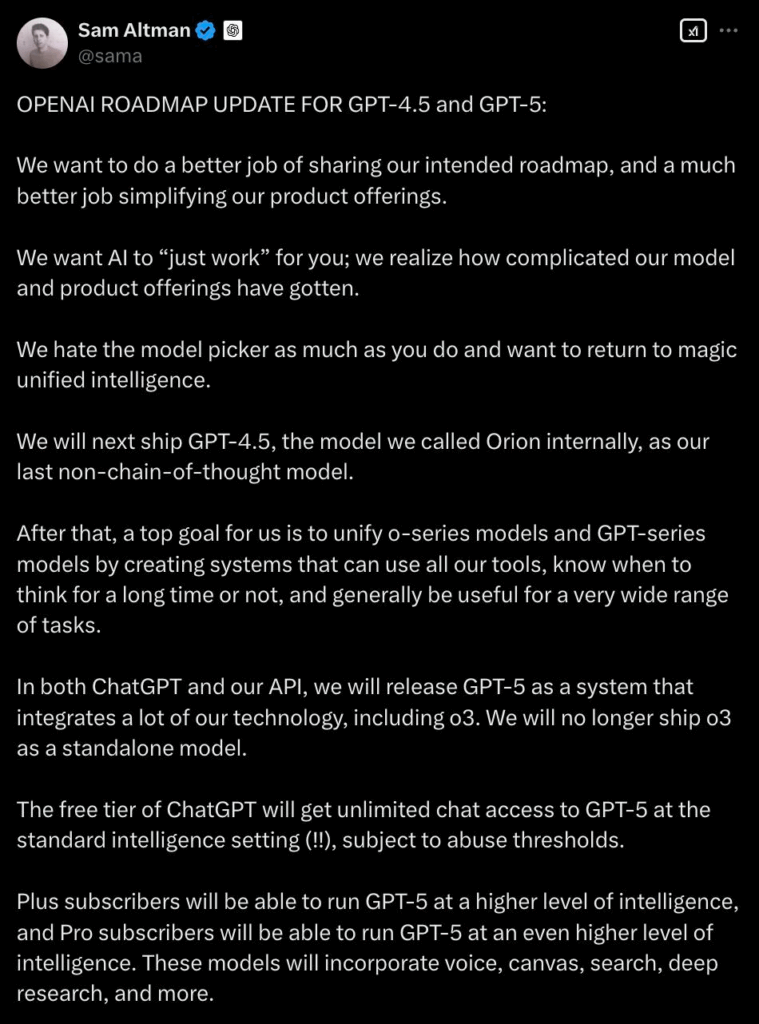
Altman recently took to X (formerly Twitter) to unveil OpenAI’s roadmap for its upcoming models, including GPT-4.5 and GPT-5. The biggest revelation? GPT-5, powered by the O3 reasoning model, will be free for all users.
a) A Return to Unified Models
In his post, Altman acknowledged that OpenAI’s previous model releases had been somewhat convoluted, with different versions like the “o-models” causing confusion. To address this, OpenAI will now return to a unified model approach—meaning the O3 model will be fully integrated into the flagship GPT-5. This move eliminates the need for separate standalone models, streamlining user experience.
Altman’s roadmap tweet did not specify an exact launch date for GPT-5, but the announcement strongly suggests that its release is imminent. Considering OpenAI’s last major flagship model was launched in March 2023, many had expected GPT-5 to be available by now. However, OpenAI appears to be taking its time to refine the model before unveiling it to the public.
b) GPT-5 Free for All—With More Perks for Paid Users
One of the most surprising aspects of Altman’s announcement is that GPT-5 will be freely accessible to all ChatGPT users—without restrictions on standard usage.
Altman confirmed:
“The free tier of ChatGPT will get unlimited chat access to GPT-5 at the standard intelligence setting (!!), subject to abuse thresholds.”
However, OpenAI is introducing tiered intelligence levels:
- Free users will have unlimited access to GPT-5 at a standard intelligence setting.
- Plus subscribers will unlock a more advanced version of GPT-5.
- Pro subscribers will gain access to GPT-5 at its highest intelligence level, along with features like voice interactions, a canvas interface, enhanced search, and deep research capabilities.
c) Deep Research Coming to Free Users—But With Limits
OpenAI is also expanding access to its premium Deep Research feature, previously exclusive to Pro subscribers. In response to a post on X, Altman clarified that Deep Research will now be available to both free and Plus users, but with some limitations.
- Free-tier users will receive two uses per month.
- Plus-tier users will receive ten uses per month.
However, OpenAI plans to scale up these limits over time. Interestingly, Altman also remarked that Deep Research is “worth $1,000 per month,” which some have interpreted as a subtle dig at Elon Musk’s recent $97 billion buyout offer for OpenAI—a deal that Altman flatly rejected with a simple “No, thank you.”
d) What This Means for OpenAI
This announcement marks a pivotal moment for OpenAI. By making GPT-5 free, the company is doubling down on accessibility and user engagement, potentially widening its lead in the AI space. At the same time, its tiered intelligence structure ensures that premium users still get access to superior capabilities—creating a sustainable business model without locking core AI advancements behind a paywall.
Moreover, OpenAI’s shift to unified models simplifies its offerings, making it easier for users to understand and leverage the full power of its AI. With DeepSeek intensifying competition and other tech giants ramping up their AI investments, OpenAI’s decision to offer free, high-quality AI services may prove to be a strategic masterstroke in retaining its dominance.
With the GPT-5 launch seemingly around the corner, one thing is clear: the AI race is far from over, and OpenAI is gearing up for a new era.
1.11 Europe’s Boldest AI Investment Yet: The €200 Billion InvestAI Initiative
The European Union has launched InvestAI, its most ambitious artificial intelligence initiative to date—a €200 billion public-private partnership designed to solidify Europe’s leadership in AI. Announced at the AI Action Summit in Paris, InvestAI aims to mobilize the largest AI investment in history, reinforcing Europe’s commitment to open innovation, safety, and technological sovereignty.
a) A Distinct Approach: Open, Collaborative, and Secure AI
While the U.S. and China dominate the AI landscape with proprietary models and closed ecosystems, Europe is carving out a different path—one rooted in openness, collaboration, and safety. Through InvestAI, the EU is fostering open-source AI development, ensuring that AI advancements remain transparent, accessible, and equitable.
At the core of this initiative are AI gigafactories—large-scale hubs inspired by the CERN model, designed to counterbalance Big Tech’s computing monopolies. These gigafactories will serve as shared research and development spaces where startups, researchers, and enterprises can access high-performance computing (HPC) resources without being locked into proprietary ecosystems. Additionally, Europe’s top technology firms are expected to play a vital role in driving AI adoption and fostering industry collaboration within the InvestAI framework.
b) Harnessing Europe’s Supercomputers and AI Talent
A defining advantage of Europe’s AI initiative is its world-class supercomputing infrastructure and highly skilled talent pool. The EU is leveraging its HPC network, home to some of the world’s most powerful supercomputers, to support large-scale AI development.
Beyond hardware, Europe is making significant investments in AI talent and skills development, ensuring that AI progress encompasses not just cutting-edge algorithms and chips, but also human expertise and ethical innovation. However, a pressing challenge remains—the brain drain to U.S. tech firms. To retain and attract top AI talent, InvestAI must offer competitive salaries, robust research incentives, and clear career growth opportunities.
c) AI Safety and Governance: The EU AI Act
One of InvestAI’s key differentiators is its strong emphasis on AI safety and governance. Unlike other regions where regulation often trails behind innovation, Europe is embedding safety and trust at the foundation of AI development through the EU AI Act.
This regulatory framework ensures that AI systems built in Europe prioritize human rights, transparency, and accountability. With €150 billion in private funding and an additional €50 billion from the EU, InvestAI is not just the largest AI public-private partnership in history—it is also one of the most ethically structured.
However, a critical question looms: Will these regulatory safeguards slow down innovation compared to the more flexible environments of the U.S. and China? Striking the right balance between oversight and agility will be crucial for Europe’s success in AI.
d) InvestAI: Redefining AI Infrastructure and Strategy
InvestAI represents more than just a massive investment—it marks a paradigm shift in AI strategy:
- Instead of centralizing AI power, the initiative democratizes access to AI infrastructure.
- Instead of pursuing AI at any cost, Europe is prioritizing ethical and responsible AI.
- Instead of waiting for Big Tech to dictate AI’s future, the EU is actively shaping the global AI landscape.
By integrating advanced computing resources, fostering industry collaboration, prioritizing AI skill development, and implementing strong regulatory foresight, InvestAI aims to position Europe as a global leader in trustworthy, impactful AI innovation.
e) Europe’s AI Future: Beyond Competition—Shaping the AI Revolution
The race for AI supremacy is far from over, and Europe has made it clear that it is not merely competing—it is leading on its own terms. InvestAI is not just about funding AI research; it is about ensuring that AI serves humanity, fosters sustainable innovation, and strengthens Europe’s standing as a global AI hub.
However, challenges remain:
- Can InvestAI achieve widespread adoption within the private sector?
- Will Europe’s regulatory framework slow down AI breakthroughs?
- Can Europe retain its best AI talent amid fierce global competition?
The answers to these questions will define the EU’s AI trajectory in the coming years. But one thing is certain: Europe is no longer a passive observer in the AI revolution—it is setting the rules for a future where AI is open, safe, and accessible to all.
Contributor:

Nishkam Batta
Editor-in-Chief – HonestAI Magazine
AI consultant – GrayCyan AI Solutions
Nish specializes in helping mid-size American and Canadian companies assess AI gaps and build AI strategies to help accelerate AI adoption. He also helps developing custom AI solutions and models at GrayCyan. Nish runs a program for founders to validate their App ideas and go from concept to buzz-worthy launches with traction, reach, and ROI.
Contributor:

Nishkam Batta
Editor-in-Chief - HonestAI Magazine
AI consultant - GrayCyan AI Solutions
Nish specializes in helping mid-size American and Canadian companies assess AI gaps and build AI strategies to help accelerate AI adoption. He also helps developing custom AI solutions and models at GrayCyan. Nish runs a program for founders to validate their App ideas and go from concept to buzz-worthy launches with traction, reach, and ROI.
Unlock the Future of AI -
Free Download Inside.
Get instant access to HonestAI Magazine, packed with real-world insights, expert breakdowns, and actionable strategies to help you stay ahead in the AI revolution.